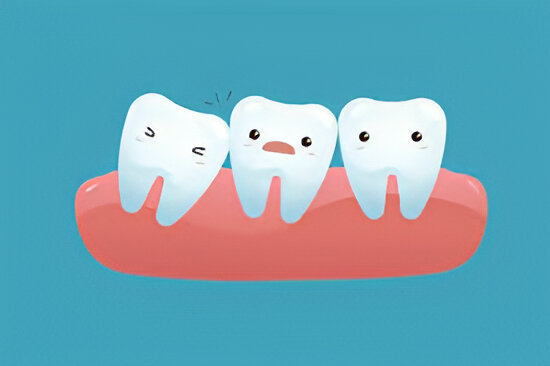
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, typically emerge between the ages of 17 and 25. While some people experience no issues, others may face complications that can lead to a Wisdom Tooth Infection. This condition is not only painful but can also result in serious oral health concerns if left untreated. Therefore, recognizing the signs early and understanding the causes can help prevent complications and guide timely treatment.
Let’s dive into everything you need to know—from symptoms and causes to when you should seek professional dental care.
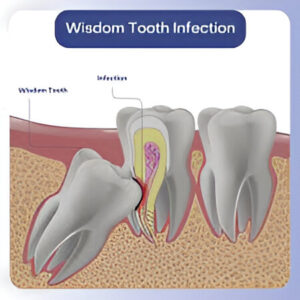
Understanding Wisdom Teeth and Why They Become Problematic
Although wisdom teeth served a purpose in our ancestral diets, modern jaw sizes have shrunk, making it difficult for these molars to erupt properly. As a result, they often become impacted, meaning they are stuck under the gum or only partially emerge. This scenario significantly raises the risk of developing a Wisdom Tooth Infection.
Impacted or misaligned wisdom teeth can:
-
Trap food and bacteria under the gumline
-
Cause damage to neighboring teeth
-
Lead to inflammation and swelling in the gum tissue
Thus, even a slightly irritated wisdom tooth should not be ignored, as it can progress to an infection quickly.
Early Symptoms of a Wisdom Tooth Infection
Fortunately, the body often gives clear signals when something is wrong. A Wisdom Tooth Infection presents various symptoms, some subtle and others hard to miss. Identifying them early is crucial to prevent escalation.
Watch out for these common symptoms:
-
Persistent pain or throbbing near the back of the mouth
-
Swelling around the jaw or face
-
Red or swollen gums near the affected area
-
Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
-
Difficulty opening your mouth or chewing
-
Pus discharge from the gums
Moreover, if you experience fever, swollen lymph nodes, or fatigue, it could be a sign that the infection is spreading, which warrants immediate dental attention.
The Main Causes Behind Infected Wisdom Teeth
You might wonder—how does a Wisdom Tooth Infection develop? In most cases, it begins when bacteria enter the gum tissue around a partially erupted tooth. However, there are a few specific triggers that increase the risk.
Key causes include:
-
Partial eruption: When a wisdom tooth breaks through only partway, it creates a flap of gum tissue where food and bacteria can accumulate.
-
Poor oral hygiene: Hard-to-reach areas around the wisdom tooth can harbor bacteria.
-
Gum disease: Existing periodontal issues may worsen around the wisdom tooth area.
-
Tooth decay: Cavities in the wisdom tooth or adjacent molars can extend into the gums.
Over time, these issues can lead to the development of pericoronitis, an inflammation of the tissue surrounding the wisdom tooth, often the root of infection.
How Is a Wisdom Tooth Infection Diagnosed?
When symptoms arise, timely diagnosis is essential. Dentists rely on both physical examinations and imaging techniques like X-rays to determine the state of your wisdom teeth. In cases of Wisdom Tooth Infection, the dentist may also examine your lymph nodes, take note of swelling, and check for fever or other systemic signs of infection.
Here’s what the diagnostic process usually includes:
-
A comprehensive oral exam
-
X-rays to view impacted or infected teeth
-
Evaluation of gum health and adjacent structures
-
Questions about your symptoms and medical history
Early diagnosis enables dentists to recommend an effective treatment plan before the infection spreads further.
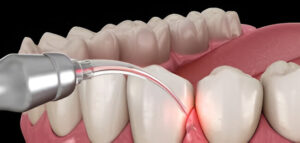
Treatment Options for Wisdom Tooth Infections
The good news is that a Wisdom Tooth Infection is treatable. Depending on the severity, your dentist may recommend one or a combination of the following:
Common treatment options:
-
Antibiotics to reduce the infection and swelling
-
Warm salt water rinses to soothe inflamed gums
-
Pain relief medications for discomfort
-
Drainage of any pus from the infected area
-
Surgical intervention is required if the tooth must be removed
In many cases, especially if the infection recurs or is severe, wisdom tooth removal becomes the most effective solution to eliminate the source of the problem.
Prevention Tips to Avoid Future Infections
While some causes are out of our control, there are proactive steps you can take to lower the risk of developing a Wisdom Tooth Infection. Prevention starts with good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups.
Here are some essential preventive measures:
-
Brush and floss twice a day, especially around the back molars
-
Use an antimicrobial mouthwash
-
Visit your dentist every six months
-
Avoid sugary foods that promote bacterial growth
-
Don’t ignore mild gum pain or irritation
Additionally, regular dental X-rays can help monitor the development and positioning of your wisdom teeth, making it easier to intervene before issues arise.
When Should You See a Dentist?
Many people delay seeking care, hoping the discomfort will subside. However, when it comes to a Wisdom Tooth Infection, postponing treatment can result in complications such as jaw stiffness, abscess formation, and even bone damage.
You should see a dentist immediately if:
-
Pain persists for more than two days
-
There is visible swelling or pus
-
You develop a fever or feel generally unwell
-
You have difficulty chewing or swallowing
Early intervention not only reduces pain but can also prevent more complex procedures in the future.
Conclusion: Don’t Wait—Take Wisdom Tooth Pain Seriously
In summary, a Wisdom Tooth Infection should never be taken lightly. From minor discomfort to full-blown infections, these issues can escalate quickly without proper care. Therefore, staying informed, recognizing early symptoms, and seeking timely treatment are all vital steps toward maintaining optimal oral health.
While antibiotics and home care may offer short-term relief, long-term solutions like wisdom tooth removal are often necessary to prevent recurring infections. And if you’re considering proactive dental health for the younger members of your family, consulting a qualified pediatric dentist early can help identify potential issues before they become serious.
So, whether you’re experiencing discomfort or just want to stay ahead of future problems, don’t hesitate to contact your dentist. After all, prevention is always better than a cure.